Categories
Label
Weekly
-
SHOULD + V1, SHOULD + V-ing, SHOULD + Have V-3 Should is a modal verb. After Should you use the base form of the infinitive (= verb ...
-
We normally use WILL to speak about the future. It is always combined with another verb. Since WILL is classified as a modal verb (li...
Mengenai Saya
Minggu, 02 April 2017
Sabtu, 01 April 2017
Conditional Sentence
Conditional Sentence Type 0
Conditional type zero is used to
talk about general truths, scientific facts or things which always happen under
certain conditions.
Form:
If + Simple Present, + Simple Present
|
Use:
The zero conditional is used to talk
about things which are always true, scientific facts, general truths:
Examples:
If you cross an international date
line, the time changes.
Phosphorus burns if you expose it to air.
If I wake up early, I go jogging.
Phosphorus burns if you expose it to air.
If I wake up early, I go jogging.
NOTE: you can use "when"
instead of "if".
Often called the "real"
conditional because it is used for real or possible situations. These
situations take place if a certain condition is met. It is possible and also very
likely that the condition will be fulfilled.
Form:
If
+ Simple Present, + Simple Future
|
Use
Conditional Sentences Type 1 refer
to the future. An action in the future will only happen if a certain condition
is fulfilled by that time. We don't know for sure whether the condition
actually will be fulfilled or not, but the conditions seems rather
realistic – so we think it is likely to happen.
Example:
If I have enough time, I'll watch
the football match.
I may have time to watch the match
but I'm not sure about it.
Often called the "unreal"
conditional because it is used for unreal impossible or improbable situations.
This conditional provides an imaginary result for a given situation. It is very
unlikely that the condition will be fulfilled.
Form:
if
+ Simple Past, + would + base verb
|
Were
/ Was
In conditional type 2, we usually
use in the if clause "were" instead of "was"
even if the pronoun is I, he, she or it. "were"
here is a subjunctive form.
NOTE "was" is also
a possible form.
Example:
If I were a millionaire, I
would buy a castle.
Use
Conditional Sentences Type 2 refer
to an action in the present that could happen if the present situation were
different. I don't really expect the situation to change because it is very
unlikely.
Example:
If I had a lot of money, I would
travel around the world.
It is impossible that the
condition will be met because it refers to the past.
Form:
if
+ Past Perfect, + would + have + Past Participle
|
Use
Conditional Sentences Type 3 refer
to situations in the past. They express hypothetical results to past given
situations.
Example:
If he had been careful, he wouldn't
have had that terrible accident.
Sometimes in the past, he was
careless. He drove so fast. So he had a terrible accident
Things to remember
1. The main clause can also be at
the beginning of the sentence. In this case, don't use a comma.
Examples:
"Phosphorus burns if you expose
it to air."
" I will send her an invitation if I find her address."
" I would travel around the world if I had a million dollars."
"He wouldn't have had that terrible accident if he had been careful."
" I will send her an invitation if I find her address."
" I would travel around the world if I had a million dollars."
"He wouldn't have had that terrible accident if he had been careful."
2. Main clause and/or if
clause might be negative.
Example:
If I don’t see him this
afternoon, I will phone him in the evening.
If he had been careful, he wouldn't have had an accident.
If he had been careful, he wouldn't have had an accident.
Jumat, 31 Maret 2017
Senin, 27 Maret 2017
Passive Voice
WHAT IS VOICE?
In English grammar, voice doesn't mean the sound you make when you speak. It shows whether the subject is doing the action, or having the action done to it.
ACTIVE VOICE
The verb is in the active voice when the subject does the action.
Example: A cat ate the fish (Subject:cat/ Verb: ate/Object: fish)
Here, the doer of the action is the cat and the verb ate is in the active voice.
When action is done to the subject, the verb is in the passive voice . The previous object (fish) is now used as the subject
Example: The fish was eaten by a cat. (Verb: eaten, Subject : fish)
Here, action is done to the subject, and the verb "was eaten" is in the passive voice.
USE OF THE THE PASSIVE VOICE
We use the action voice whenever we can.
We use the passive when:
* We want to make the active object more important
* We do not know the active subject
* We prefer not naming
Note that we always use by to introduce the passive object.
Example: Fish are eaten by cats
We use 'by' only when we have to
VERBS WITH TWO OBJECTS
A verb can have two objects- a person and a thing. Such a verb can have two possible passive voices.
Example 1:
Active: The salesmen shows Nick a new computer./ The salesmen shows a new computer to Nick.
Passive: Nick is shown a new computer. / A new computer is shown to Nick
Example 2:
Active: We lent Bob some money./ We lent some money to Bob.
Passive: Bob was lent some money. / Some money was lent to Bob.
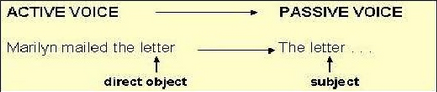
CHANGING ACTIVE TO PASSIVE
In changing a sentence from active voice to one in passive voice, we make the object of the passive
voice sentence the subject of the passive voice sentence.
The verb used in a passive voice sentence is formed by adding the past participle to "to be" (am, is, are, was, were, has been, have been, will be, etc.)
Passive verbs have the same tenses (simple present tense, present continuous tense, present perfect tense, etc as the active verbs.)
Only verbs which take on an object can be changed to the passive.
Examples: He runs away. (This sentence has no object, so it's not possible to turn it into a passive sentence.)
Here are the examples of sentences in active voice and passive voice in the present tense.

Examples of sentences in active voice and their equivalent sentence in the passive voice in the past tense are shown in this table.

MODALS AND INFINITIVE
Will /Can / Must / Have to etc. + be + Past Participle

In English grammar, voice doesn't mean the sound you make when you speak. It shows whether the subject is doing the action, or having the action done to it.
ACTIVE VOICE
The verb is in the active voice when the subject does the action.
Example: A cat ate the fish (Subject:cat/ Verb: ate/Object: fish)
Here, the doer of the action is the cat and the verb ate is in the active voice.
When action is done to the subject, the verb is in the passive voice . The previous object (fish) is now used as the subject
Example: The fish was eaten by a cat. (Verb: eaten, Subject : fish)
Here, action is done to the subject, and the verb "was eaten" is in the passive voice.
USE OF THE THE PASSIVE VOICE
We use the action voice whenever we can.
We use the passive when:
* We want to make the active object more important
* We do not know the active subject
* We prefer not naming
Note that we always use by to introduce the passive object.
Example: Fish are eaten by cats
We use 'by' only when we have to
VERBS WITH TWO OBJECTS
A verb can have two objects- a person and a thing. Such a verb can have two possible passive voices.
Example 1:
Active: The salesmen shows Nick a new computer./ The salesmen shows a new computer to Nick.
Passive: Nick is shown a new computer. / A new computer is shown to Nick
Example 2:
Active: We lent Bob some money./ We lent some money to Bob.
Passive: Bob was lent some money. / Some money was lent to Bob.
CHANGING ACTIVE TO PASSIVE
In changing a sentence from active voice to one in passive voice, we make the object of the passive
voice sentence the subject of the passive voice sentence.
The verb used in a passive voice sentence is formed by adding the past participle to "to be" (am, is, are, was, were, has been, have been, will be, etc.)
Passive verbs have the same tenses (simple present tense, present continuous tense, present perfect tense, etc as the active verbs.)
Only verbs which take on an object can be changed to the passive.
Examples: He runs away. (This sentence has no object, so it's not possible to turn it into a passive sentence.)
Here are the examples of sentences in active voice and passive voice in the present tense.
Examples of sentences in active voice and their equivalent sentence in the passive voice in the past tense are shown in this table.
Will /Can / Must / Have to etc. + be + Past Participle
VIDEO OF PASSIVE VOICE LESSON
Langganan:
Komentar (Atom)
Weekly
-
SHOULD + V1, SHOULD + V-ing, SHOULD + Have V-3 Should is a modal verb. After Should you use the base form of the infinitive (= verb ...
-
We normally use WILL to speak about the future. It is always combined with another verb. Since WILL is classified as a modal verb (li...